Understanding Recurrent Pneumothorax Treatment

Pneumothorax, an accumulation of air in the pleural space, can lead to significant respiratory complications. Particularly, recurrent pneumothorax poses substantial challenges for patients, necessitating thorough understanding and effective treatment options. This guide provides comprehensive insights into the best practices for treating recurrent pneumothorax, ensuring patients receive optimal care.
What is Recurrent Pneumothorax?
A recurrent pneumothorax refers to the repeated occurrence of pneumothorax episodes, typically following an initial event. While it can occur in individuals without underlying lung disease, it is commonly seen in those with conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or interstitial lung disease. Understanding the causes and symptoms is critical for effective management and treatment.
Symptoms of Pneumothorax
Recognizing the symptoms of pneumothorax early can greatly influence treatment outcomes. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden chest pain: This is often sharp and may be worse with deep breathing.
- Shortness of breath: Patients may experience difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Rapid breathing: A high respiratory rate may accompany the distress.
Diagnosis of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Prompt diagnosis is essential to initiate appropriate treatment. Diagnostic methods include:
- Physical examination: Doctors will check for decreased breath sounds on the affected side and possible subcutaneous emphysema.
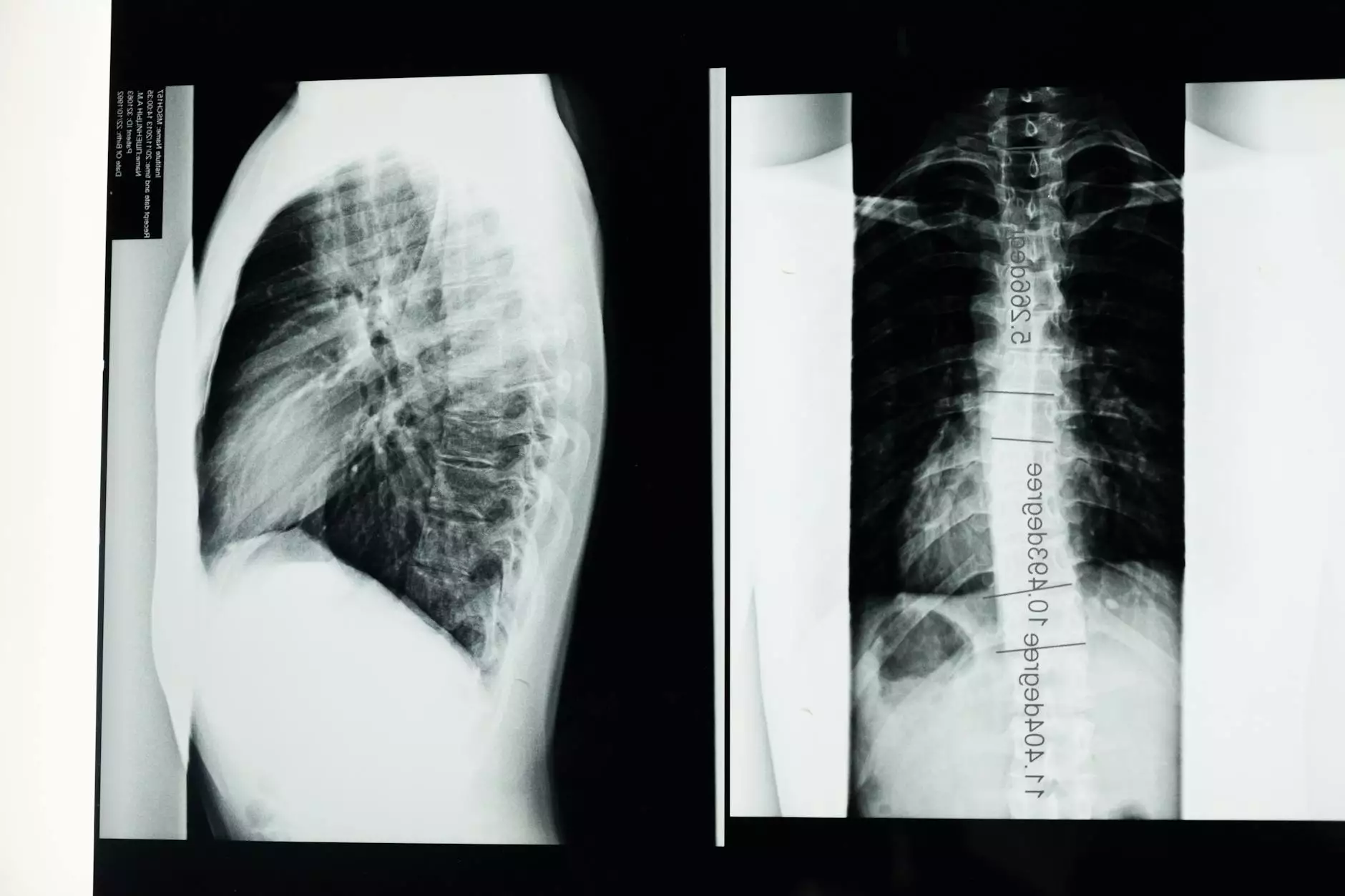
- Imaging studies: Chest X-rays and CT scans are crucial for confirming the diagnosis and assessing the size of the pneumothorax.
Treatment Options for Recurrent Pneumothorax
When it comes to the treatment of recurrent pneumothorax, various options are available, ranging from conservative measures to surgical interventions. The choice of treatment is typically based on the severity, frequency, and underlying lung conditions.
1. Conservative Management
In cases of small pneumothoraxes, the treatment may be conservative. This includes:
- Observation: Many small pneumothoraxes resolve spontaneously without intervention.
- Supplemental oxygen: Administering oxygen can enhance reabsorption of the air in the pleural space.
2. Needle Aspiration
If the symptoms are significant or if the pneumothorax does not resolve, needle aspiration may be performed. This procedure involves:
- Inserting a needle: A needle is inserted into the pleural space to evacuate the trapped air.
- Quick relief: This method can provide rapid relief of symptoms.
3. Chest Tube Placement
For larger pneumothoraxes or those that do not respond to needle aspiration, chest tube placement may be necessary. This procedure involves:
- Inserting a tube: A tube is inserted into the pleural space to continuously drain air and fluid.
- Restoration of lung function: The goal is to re-expand the lung and restore its normal function.
Surgical Options for Recurrent Pneumothorax
In cases of recurrent pneumothorax, surgery may be the most effective treatment to prevent future episodes. Common surgical options include:
1. Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
VATS is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat recurrent pneumothorax through:
- Small incisions: Only small incisions are made in the chest wall for surgical access.
- Surgical techniques: Techniques employed may include pleurodesis, where a substance is introduced to adhere the lung to the chest wall thereby preventing future pneumothoraxes.
2. Thoracotomy
In more severe cases, a traditional thoracotomy may be performed, which involves:
- Large incision: A larger incision allows for direct access to the lungs.
- Comprehensive treatment: This option allows for more extensive procedures to repair lung lesions that may contribute to recurrent issues.
Preventive Measures
Preventing recurrent pneumothorax is critical for individuals at risk. Key preventive strategies include:
- Avoiding risk factors: Steering clear of high-risk activities such as scuba diving.
- Smoking cessation: For smokers, quitting can significantly reduce the chances of complications.
- Regular follow-ups: Patients with a history of pneumothorax should maintain regular check-ups with their healthcare providers.
Patient Perspective: Living with Recurrent Pneumothorax
Living with the fear of recurrent pneumothorax can be distressing for patients. Understanding treatment options and having a supportive healthcare team can significantly improve quality of life. Patients are encouraged to:
- Educate themselves: Knowledge about the condition enables informed decisions regarding their health.
- Keep a symptom diary: Recording symptoms can help healthcare providers tailor treatment more effectively.
- Seek emotional support: Support groups and counseling can assist patients in coping with the emotional aspects of their condition.
Conclusion: Effective Management of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Recurrent pneumothorax requires a comprehensive understanding of treatment options tailored to individual needs. At Neumark Surgery, our expertise in managing complex thoracic conditions ensures you receive the highest standard of care. From initial diagnosis to advanced surgical options, we prioritize patient health and recovery.
For those looking for reliable information and treatment options for recurrent pneumothorax, consult our dedicated team of medical professionals. Together, we can navigate the path to recovery and significantly improve your lung health.
recurrent pneumothorax treatment